Mean Absolute Risk for Gain Normal Independent (meanabs_risk_ni_g)
Mean Absolute Risk for Gain Normal Independent. Mean Absolute for Gain when all coefficients in Linear Loss function are independent normally distributed random values.. (Mean Absolute for Gain Normal Independent) = - Average Loss + Mean Absolute Deviation.
Syntax
meanabs_risk_ni_g(matrix_mn,matrix_vr) |
short call |
meanabs_risk_ni_g_name(matrix_mn,matrix_vr) |
call with optional name |
Parameters
matrix_mn is a PSG matrix of mean values:

where the header row contains names of variables. The second row contains numerical data.
matrix_vr is a PSG matrix of variance values:
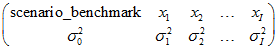
where the header row contains names of variables. The second row contains numerical data.
Mathematical Definition
Mean Absolute Risk for Gain Normal Independent function is calculated as follows:
![]() ,
,
where
![]() is Mean Absolute Deviation Normal Independent function,
is Mean Absolute Deviation Normal Independent function,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() is probability density function of the standard normal distribution.
is probability density function of the standard normal distribution.
Example
See also
Mean Absolute Error, Mean Absolute Error Normal Independent, Mean Absolute Error Normal Dependent, Mean Absolute Risk, Mean Absolute Risk for Gain, Mean Absolute Risk Normal Independent, Mean Absolute Risk Normal Dependent, Mean Absolute Risk for Gain Normal Dependent, Mean Absolute Deviation, Mean Absolute Deviation Normal Independent, Mean Absolute Deviation Normal Dependent
